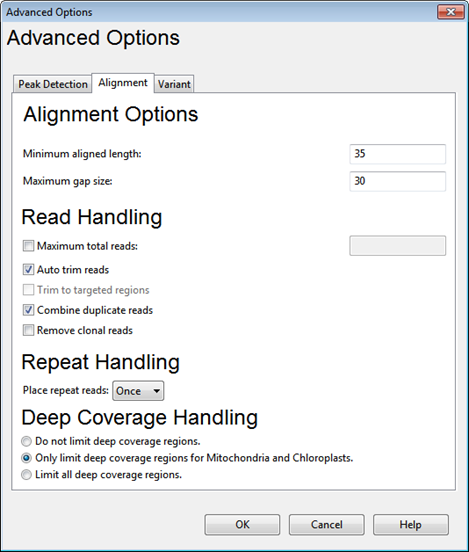
Clicking the Advanced (Assembly) Options button from certain versions of the Assembly Options dialog launches a multi-tabbed Advanced Assembly Options dialog. This help topic describes options available in the Alignment tab.

Default parameters in this tab are optimized for the sequencing technology and project type that you specified elsewhere in the wizard. Because of this, values seldom need to be changed.
Alignment Options:
•Minimum aligned length – The minimum length of at least one aligned segment of a read after trimming. The default value varies depending on the read technology you selected.
•Maximum gap size – The maximum number of gaps allowed per 1000 bases in the alignment.
Read Handling:
•Maximum total reads – Check the box and enter a value if you wish to limit the read depth. Utilizing this option can make the assembly proceed faster.
•Auto trim reads – If this box is checked, the ends of reads are trimmed to best match alignment to the template. SeqMan NGen will mark the portion of the read that aligns well to the template, and will set the trimming to skip any of the poorly aligning parts of the read. Checking this option optimizes the end trimming of reads to maintain as much of the read as possible, while still meeting the minimum match percentage threshold. However, checking the box can also lead to the removal of true variant bases located near the ends of reads. The box is checked by default.
•Trim to targeted regions – This box is only enabled for workflows that offer the ability to add a .bed file, and where a .bed file was specified in the Input Reference Sequences screen If this box is checked, reads extending beyond the 5’ or 3’ end of a targeted region will be trimmed to the target boundary. The box is unchecked by default.
•Combine duplicate reads – Duplicate reads are those which share the same starting position and the same sequence. Check this box if you wish to combine the reads and only enter one of them into the alignment. Any duplicates will be scored but not aligned. Combining duplicate reads collapses reads with identical sequences with the same start and stops and replaces them with a single entry with a suffix “[dup #]” where # is the number of collapsed reads. However, this option does not take the location of a paired end read into consideration. It is used primarily to reduce issues with alignment and visualization of very deep sequence regions, typical of RNA-Seq data for highly expression genes.
•Remove clonal reads – Clonal reads, where the sequence and endpoints of both reads in a pair match those in another pair, are usually the result of PCR artifacts. Check this box if you wish to retain one of the pairs in the assembly, but completely remove the clones (duplicate pairs) after the alignment phase of assembly. If the box is checked, cloned reads will not be scored, and will not be included in SNP calculation or gene quantification. This option can be useful in genome/exome/gene panel sequencing workflows where clonal reads can skew variant calculations. Checking the box may add substantially to the time required for assembly.
Checking this option does not remove a pair if its two reads are duplicates of different pairs. It only removes duplicate pairs if the entire pair is completely identical to another pair. For example, SeqMan NGen will not remove a pair whose forward read is a duplicate of a read from pair A, but whose reverse read is a duplicate of a read from pair B.
Note: Do not check both Combine duplicate reads and Remove clonal reads, as this will lead to unpredictable results due to the order in which SeqMan NGen removes clones and combines duplicates.
Repeat Handling:
•Place repeated reads – Choose to place repeated reads Once, All or Never. The default is All for the Metagenomics/population assembly workflow and Once for all other workflows.
Deep Coverage Handling:
The way in which very deep coverage is handled can greatly affect assembly time. For example, if unlimited deep coverage is allowed, it could take upwards of eight hours to align human NA24385 sequences (Genome in a Bottle “Ashkenazim Trio Son”) to the mitochondrial (MT) genome. That is because most of that human sample has a coverage depth of 35,000. In such a case, limiting deep coverage regions can allow the assembly to proceed much more quickly.
This section of the Alignment tab dialog lets you specify whether and when to filter deep coverage regions. The default selection is made automatically by SeqMan NGen based on the current workflow. However, you may make any desired selection.
•Do not limit deep coverage regions –With the exceptions described below, this is the default for most templated workflows.
•Only limit deep coverage regions for Mitochondria and Chloroplasts –The default for all assemblies using templates that include mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes.
•Limit all deep coverage regions – The default for all miRNA and microbial genome workflows.
*******************
When you have made the desired selections in this tab of the Assembly Options dialog, click another available tab to make changes there. If you don’t need to make further changes, click OK to close the Advanced Assembly Options dialog and return to the Assembly and Signal Processing or Assembly Options screen.