The Sanger Validation workflow allows you to co-assemble non-Sanger and Sanger data in SeqMan NGen, and then view the results in SeqMan Pro. This workflow will save data in .sqd format as long as there are fewer than 10M reads.
There are two circumstances where you may wish to create this type of hybrid assembly:
•To use Sanger reads to validate SNPs in non-Sanger (usually Illumina) assemblies.
•To close gaps in genome workflows.
Creating the assembly in SeqMan NGen:
1) In the Choose Assembly Workflow screen, select either Whole Genome or Exome and Gene Panel.
2) In the Choose Assembly Type screen, choose Sanger Validation.
3) In the Input Reference Sequences screen, add the reference sequence. Both VCF and Targeted regions file boxes are checked by default, and can be unchecked if not needed. See Make a Custom VCF File for more information about the VCF file type.
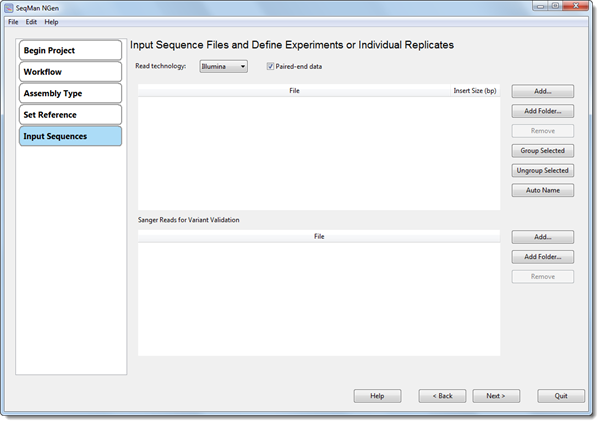
4) In the Input Sequence Files and Define Experiments or Individual Replicates screen, specify the Read technology and paired-end status of the non-Sanger reads. In the upper section, add the non-Sanger reads and then name and group them as usual. In the lower section, add the Sanger reads.

5) Proceed through the remaining wizard screens as you would for any workflow, then initiate the assembly.
Using Sanger data to confirm non-Sanger reads in SeqMan Pro:
1) After the assembly is complete, open the .assembly in SeqMan Pro.
2) Double-click on the contig name in the Project window to open it in the Alignment View.
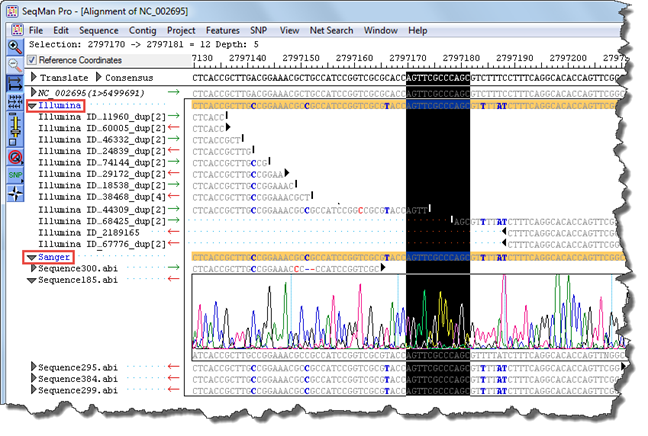
3) Scroll to the area of interest (e.g., a SNP or a gap in the data).
4) Click on an arrow next to a Sanger .abi read file to open the trace file. If prompted, navigate to the directory where the .abi file is stored.
The Sanger data can now be used to validate the non-Sanger findings.
Example: In the image below, there is a gap in the contig that is not covered by the Illumina paired-end data. In addition, blue text denotes the presence of several SNPs (i.e., locations in which the Illumina consensus does not match the template). The Sanger data corroborates these SNPs and also allows closure of the gap.