MegAlign Pro’s feature mapping lets you map a single annotation or all annotations from a source sequence to a target sequence. The sequences involved must have been previously aligned. During the process, you may optionally filter annotations so as to include/exclude specific gene types. Feature mapping is most commonly used to map desired annotations from a “completely annotated” sequence to a closely-related but “incompletely annotated” one.
The following video provides a short overview on feature mapping:
To map features from one or more source sequences to a target sequence:
- In Column 1 of the table below, locate the row that describes the target sequence—the sequence that will be “receiving” features from one or more other sequences.
- As directed in Column 2, select one or more features or one or more sequences that will act as the source(s) for the features.
- To select an individual feature, open the tracks for the sequence and click on the feature. To select two or more features, select them using Ctrl+click (Win) or Cmd+click (Mac).
- To select one or more sequences from the Overview or Sequences View, use click, Shift+click, Ctrl+click (Win), or Cmd+click (Mac).
- To select an individual feature, open the tracks for the sequence and click on the feature. To select two or more features, select them using Ctrl+click (Win) or Cmd+click (Mac).
- As directed in Column 3, use the specified Features menu command, or the corresponding “right-click” context menu command.
| Column 1: Target sequence | Column 2: Sequence or feature selection | Column 3: Command name |
|---|---|---|
| All sequences other than the designated reference | All features or selected features in the designated reference sequence (see Compute Variants) | Features > Map (Selected) Feature(s) from Reference |
| Active consensus | One or more features; or one or more source sequences. Note that feature segments falling entirely within a gap will not be copied. | Features > Map (Selected) Feature(s) to Active Consensus |
| Sequence in the top row of the view | A single feature; or one or more source sequences, none of which may be the sequence in the top row of the view. | Features >) Map (Selected) Feature(s) to Top Sequence |
| Sequence that is higher on the list than the source sequences | One or more features; or the target sequence and one or more source sequences. | Features > Map (Selected) Feature(s) to Top Selected Sequence |
| Sequence that is lower on the list than the source sequences | One or more features; or the target sequence and one or more source sequences. | Features > Map (Selected) Feature(s) to Bottom Selected Sequence |
| Sequence in the bottom row of the view | One or more features; or one or more source sequences, none of which may be the sequence in the bottom row of the view. | Features > Map (Selected) Feature(s) to Bottom Sequence |
- If more than two sequences are selected, the following popup will appear. Select Yes to launch the Map Features dialog and map all features from the specified source sequences to the target sequence; or No to abort feature mapping.
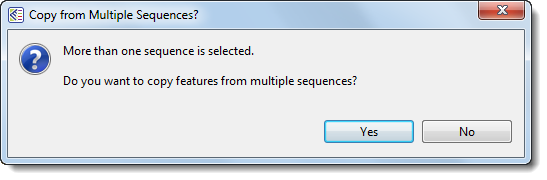
If you initiate feature-mapping for one or more individual features, MegAlign Pro maps the specific feature(s) you requested without further input.
When mapping a single feature, or mapping to the consensus, mapping happens automatically, without launching a wizard. If you initiate feature-mapping in other situations, a wizard may appear. This Map Features wizard has three screens—Features, Options and Output described in a separate topic. To navigate between the three wizard screens, either use the Back or Next buttons or click on the screen name in the left panel of the wizard.
Things to note when mapping features:
- It is possible to map multiple copies of features to any sequence, including the consensus. For example, if you first map a single feature to the consensus, then later map all features from the same source sequence, the first feature that was added will appear twice on the consensus. Be aware of this, in case you wish to avoid adding multiple copies of the same feature.
- When mapping features to the consensus in Mauve multi-block alignments, only features within the active block are mapped. When mapping features to a sequence, features in all the blocks are mapped.
- The project directory will be organized into sub-directories when 1) there are multiple source sequences, or 2) any of the source sequences are multiple end-to-end sequences, or 3) the target includes multiple end-to-end sequences.
Need more help with this?
Contact DNASTAR


